Digital Traceability | Importance | How it Works | Key Technologies | Investment Opportunities | Blockchain
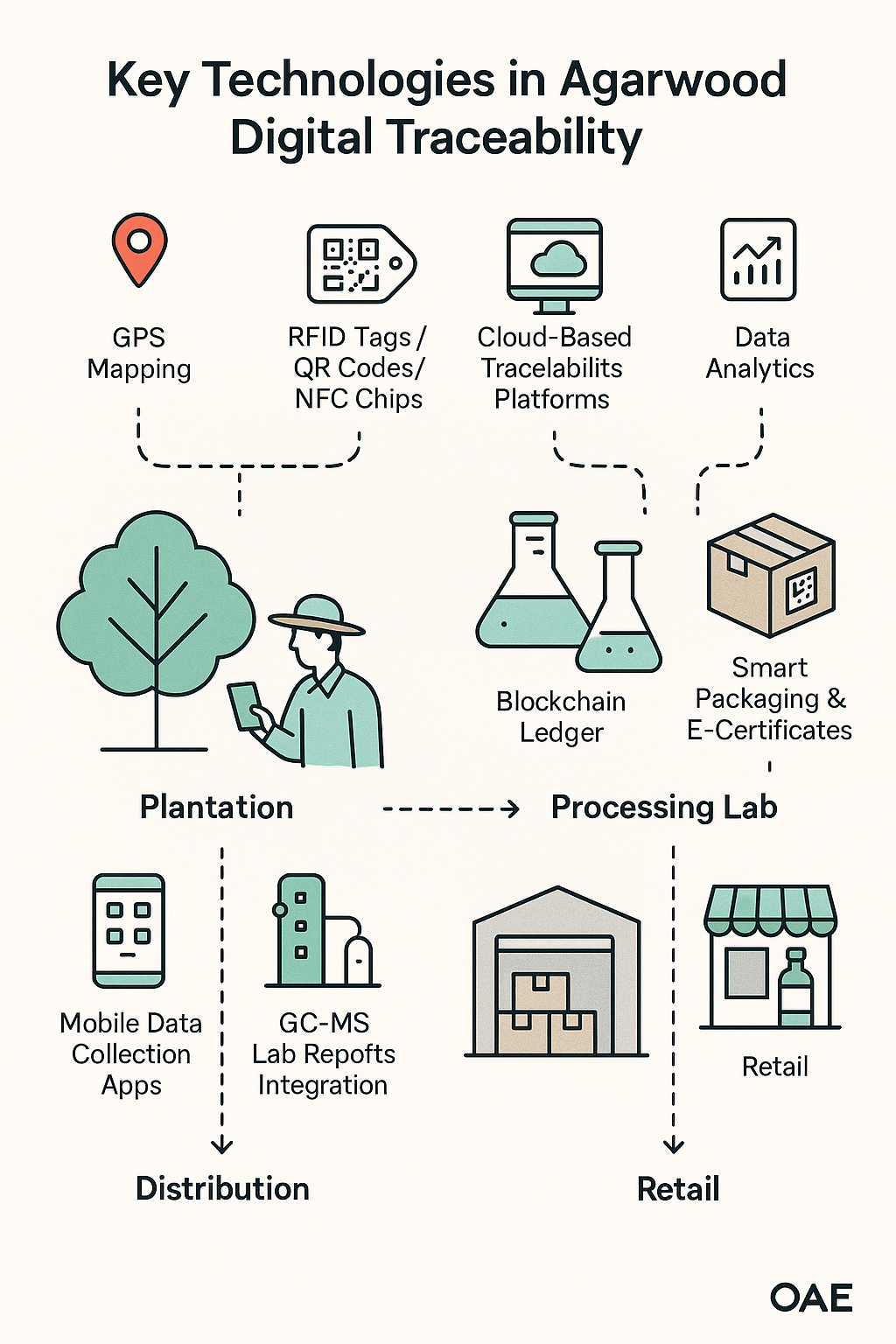
1. GPS Mapping & Geotagging
- Used for registering plantation locations
- Provides spatial data for land validation, monitoring, and harvest planning
- Ensures traceability of source to a specific geographic origin
2. RFID Tags / QR Codes / NFC Chips
- Attached to individual trees, logs, and product packages
- Store and transmit data like tree ID, owner info, harvest status, and inoculation logs
- Enable mobile scanning for real-time tracking and verification
3. Cloud-Based Traceability Platforms
- Centralized systems to collect, store, and manage traceability data
- Accessible to authorized users (farmers, inspectors, processors, exporters)
- Supports audit trails, analytics, and certification uploads
4. Mobile Data Collection Apps
- Used by farmers or field technicians to record events in real time (e.g., inoculation, harvest)
- Can function offline and sync data once connected
- Equipped with photo, GPS, timestamp, and checklist features
5. Blockchain Ledger (Optional)
- Adds tamper-proof digital integrity to supply chain data
- Ideal for premium products and export verification
- Ensures data cannot be altered once recorded
6. GC-MS Lab Reports Integration
- GC-MS (Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry) profiles can be digitally linked to batches
- Adds scientific authentication of oil quality
- Supports product differentiation and branding
7. Smart Packaging & E-Certificates
- Product labels include scannable traceability IDs
- Buyers receive digital certificates of origin, sustainability, and compliance
- Enables product verification through web or app platforms
8. AI & Data Analytics (Emerging)
- Analyze field data for resin yield prediction, inoculation success rates, or climate-related trends
- Helps optimize protocols and plantation planning
