Digital Traceability | BlockChain | BlockChain-Backed Traceability | NFT Ecosystem
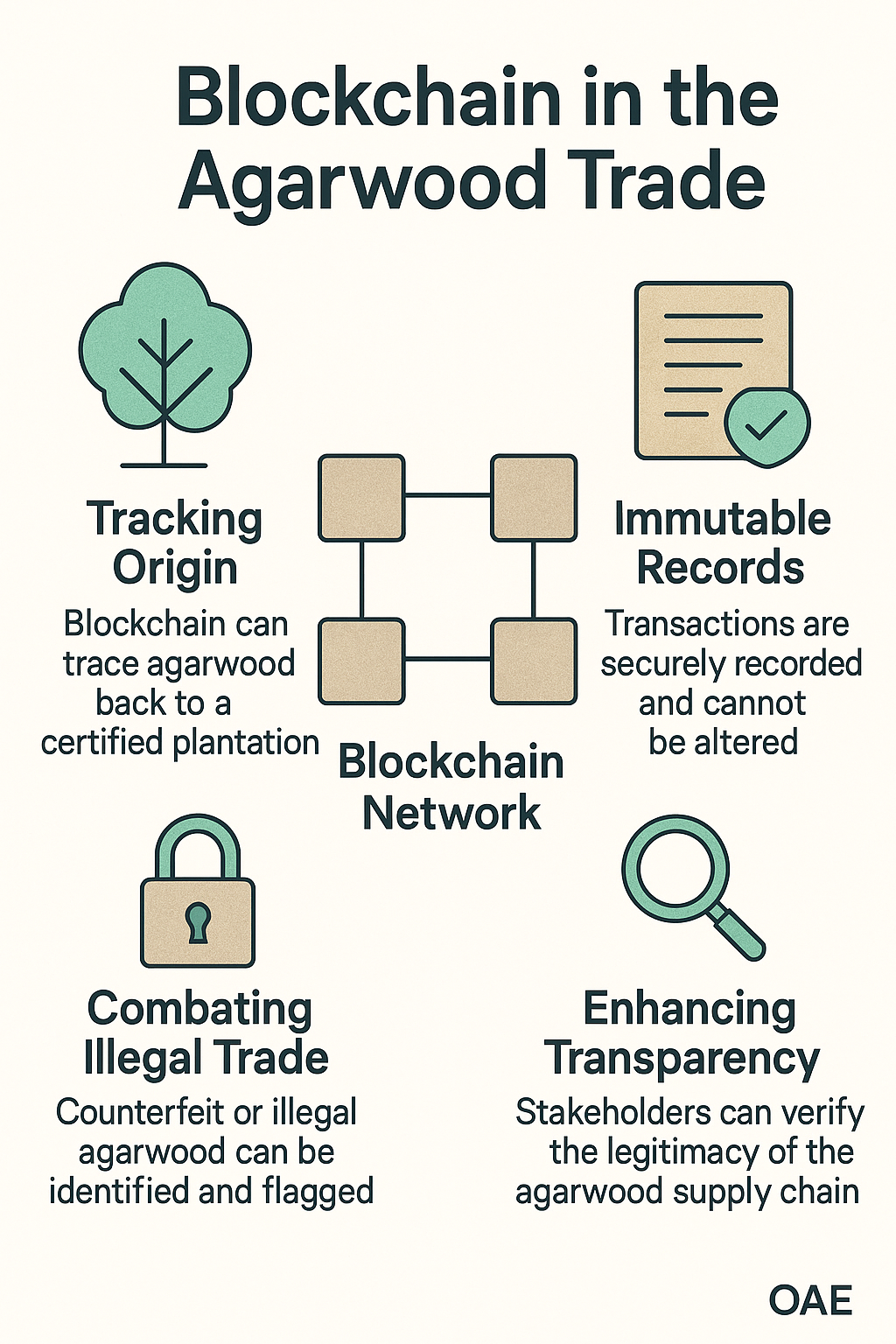
Industry Challenges in the Agarwood Trade:
- Illegal Trade & Poaching – High-value agarwood is often harvested illegally, leading to biodiversity loss and unsustainable practices.
- Lack of Traceability – Traditional supply chains make it difficult to verify the origin of agarwood, leading to regulatory violations and smuggling.
- Counterfeit & Adulterated Products – Many products in the market are diluted or misrepresented, reducing consumer trust and market value.
- Regulatory & Compliance Issues – Governments and conservation groups struggle to enforce legal sourcing due to gaps in tracking and documentation.
- Unfair Compensation for Farmers – Small-scale growers often receive minimal profits due to middlemen and lack of transparency in pricing.
How Blockchain Solves These Issues:
- Immutable Digital Ledger – Ensures that every transaction and movement of agarwood is recorded permanently, preventing fraud and unauthorized alterations.
- Smart Contracts – Automates payments and ensures fair compensation to farmers and suppliers upon meeting specific conditions (e.g., CITES compliance).
- Real-Time Digital Traceability – QR codes, RFID, or NFC technology enables tracking from tree to perfume bottle, ensuring product authenticity.
- Compliance with Global Standards – Facilitates adherence to CITES, government regulations, and sustainability certifications.
- Enhanced Consumer Trust – Buyers can verify product authenticity and ethical sourcing through a transparent blockchain ledger.
This integration of blockchain technology into the agarwood supply chain ensures a secure, ethical, and transparent global trade, benefiting farmers, traders, and consumers alike.