Fungal Inoculation | Fungal Pathogens | Bio-Inoculants Formulation | Physico-Chemical | Risk Management
Risk management in the context of Agarwood production, especially when using microbial or chemical inoculation techniques, is essential for ensuring healthy plantations, quality resin yield, and long-term sustainability.
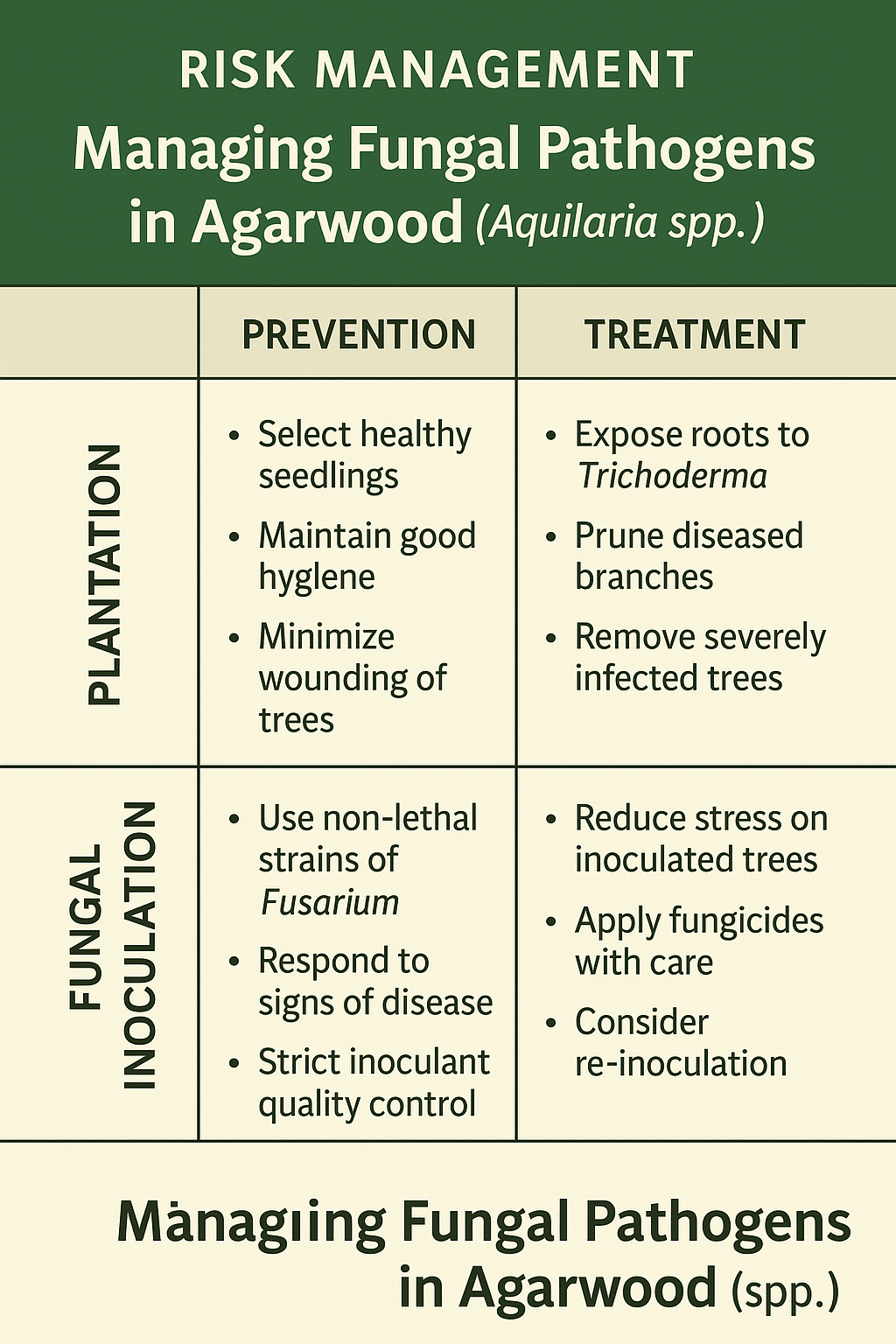
Key Risk Areas in Agarwood Production
| Risk Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Biological Risks | Pests, pathogens, over-infection from inoculants | Fungal overgrowth, tree mortality |
| Environmental Risks | Natural conditions affecting tree health | Drought, floods, typhoons |
| Operational Risks | Errors in inoculation, maintenance, harvesting | Poor injection technique, late resin extraction |
| Technical Risks | Failure of technology or poor formulation | Contaminated inoculants, blocked vessels |
| Regulatory/Legal Risks | Violations in permits, export compliance (e.g., CITES) | No DENR-EMB clearance, unregistered DNA barcode |
| Market Risks | Price volatility, low buyer demand, export bans | Market saturation, Middle East buyer delays |
Risk Management Strategies
| Strategy | Details |
|---|---|
| Pre-Inoculation Inspection | Assess tree health, age, and readiness for inoculation. |
| Sterile Protocols | Use sterilized tools, clean inoculants to prevent cross-contamination. |
| Weather Monitoring | Time inoculations before dry seasons to avoid waterlogging/flood stress. |
| Proper Dosage | Follow calibrated volumes per tree species/age. |
| Resin Monitoring Plan | Regularly check for resin formation and tree response. |
| Compliance Management | Secure CNC/ECC, BMB/CITES permits, and DNA sequencing for legality. |
| Diversified Buyers | Establish multiple buyer channels to reduce market dependency. |
